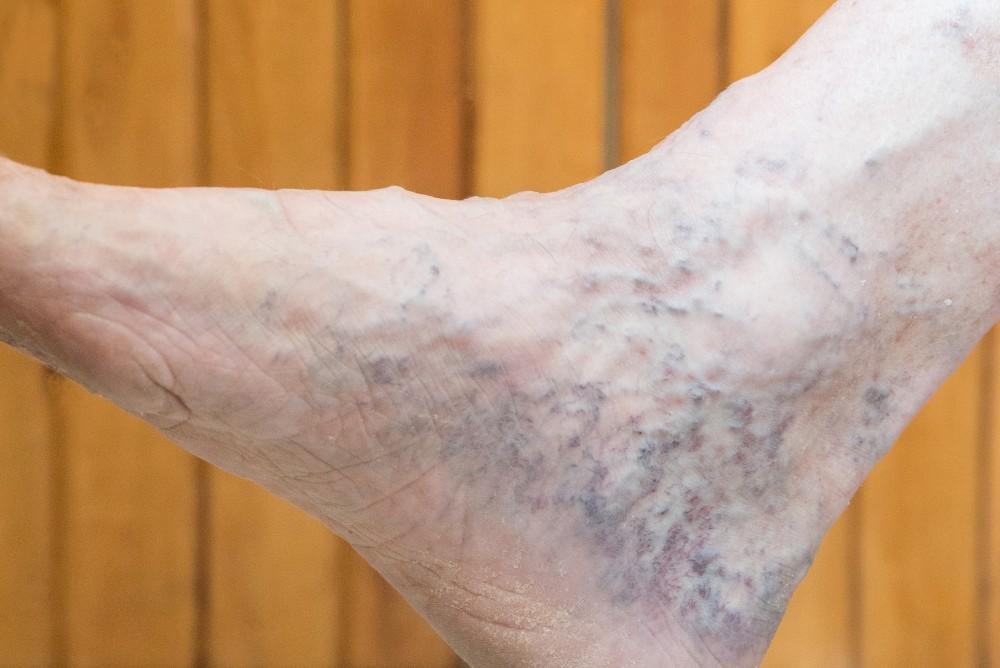
Varicose veins are a common problem that you may want to treat for cosmetic reasons or to alleviate any pain or discomfort caused by them.
Sclerotherapy is the most often used varicose vein treatment, followed by laser treatment. However, you can manage them at home by walking or wearing compression stockings.
Several types of doctors can assist you if you seek professional therapy to remove varicose veins.
Types of medical professionals
Varicose veins are treated by a variety of medical specialists, including:
Vascular surgeons
Vascular surgeons address disorders affecting blood vessels, such as varicose veins.
They can do all surgical and minimally invasive varicose vein removal methods. They can also provide consultations to determine whether you should explore any nonsurgical options first.
Phlebologists
Phlebologists are experts in diagnosing, preventing, treating, and rehabilitating venous disorders. Any surgeon, dermatologist, or general practitioner with the necessary training can become a phlebologist.
A phlebologist, for example, could be a general practitioner who is board-certified in phlebology.
Vascular or interventional radiologists
Interventional radiologists are doctors who have completed an additional 6 to 7 years of training in minimally invasive techniques. To diagnose conditions, they may employ X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs.
They can treat varicose veins using endovenous laser therapy or radiofrequency ablation.
Dermatologists or dermatologic surgeons
Dermatologists normally treat skin diseases; however, they may also treat some forms of varicose veins.
They are qualified to use sclerotherapy and laser treatment, for example.
General practitioners or family doctors
Some forms of varicose veins may be diagnosed and treated by your primary care physician. They might also suggest lifestyle modifications that can help ease symptoms, such as increasing physical activity or using compression stockings.
They can also evaluate your veins and refer you to a professional for treatment.
Treatment options
There are numerous treatment options for varicose veins, including:
- Sclerotherapy: This minimally invasive vein treatment method includes injecting a saline-containing customized solution straight into the afflicted vein. Because of the fluids, the vein seals up and finally disintegrates. It is now the most popular method of treating varicose veins.
- Laser treatment: This is the second most prevalent procedure for varicose veins. A doctor utilizes laser radiation to infiltrate the vein from the outside, gradually dissolving it.
- Radiofrequency ablation: This is yet another non-invasive treatment. Radiofrequency energy is used to break down the targeted vein.
- Endovenous laser therapy: This is a more intrusive operation that involves using laser energy to seal off the problematic vein. Instead of targeting the veins from the outside, the doctor will make a small incision that allows direct entry into the vein. This is especially useful for bigger veins that may be difficult to remove using other procedures.
Most of these treatments take multiple sessions to achieve the desired outcomes. The size and severity of your varicose veins determine the number of treatments required.
There are also strategies for dealing with them at home. These measures can alleviate any pain and discomfort they may cause, keep current ones from worsening, and prevent new ones from developing:
- Compression stockings: These socks apply pressure to the legs, increasing blood flow and alleviating edema and discomfort.
- Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can enhance blood flow and reduce vein pressure. Walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga are highly advised since they place less strain on the veins than high-impact exercises like running.
- Maintaining a moderate weight: Excess weight can strain the body, worsening existing varicose veins and increasing your risk of developing new ones.
- Elevating your legs: Keeping your legs raised when sitting or lying down will increase blood flow, minimize pain, and prevent varicose veins from worsening.