Hernia is one of the most common diseases accompanied by changes in the abdominal wall. This condition occurs when internal organs or tissues protrude from the abdominal cavity through weak points in the muscles or connective tissue. This can lead to pain, discomfort, and serious complications such as a strangulated hernia that requires immediate surgery. Over the past few decades, laparoscopic hernia surgery has become a popular treatment method that combines minimal intervention with high efficiency.
Types of hernia
Before considering laparoscopic hernia treatment methods, it is important to know the types of hernia:
- Inguinal hernia. This is the most common type of hernia and occurs in the groin when a piece of intestine or fatty tissue passes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall.
- Umbilical hernia. It usually occurs in the umbilical region and can be congenital or develop in adults, especially after pregnancy.
- Abdominal hernia of the white line. This protrusion runs through a weak spot in the midline of the abdomen where muscle fibers meet.
- Postoperative hernia. It occurs with a previous surgical incision when the scar tissue weakens, allowing organs to migrate out of the abdominal cavity.
All of these types of hernias require surgery to prevent complications, and laparoscopic surgery has become an important treatment option.
Advantages of laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic hernia surgery offers many advantages over traditional open surgical methods:
- Minimal tissue damage. Unlike open surgery, which requires a large incision, laparoscopic surgery is performed through several small openings, minimizing tissue damage.
- Less pain and discomfort. Due to fewer incisions and minimal tissue exposure, patients experience less pain after surgery.
- Faster recovery. Because laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, patients generally recover faster and can resume daily activities sooner.
- Lower risk of infection. With fewer incisions, there is less chance of infection, making the procedure safer.
- Aesthetic result. Laparoscopic surgery leaves small scars, which is especially important for patients who are concerned about their body image.
- High accuracy. With the laparoscopic method, the surgeon examines the internal organs using a special camera with a magnified image, which makes the operation more precise and safer.
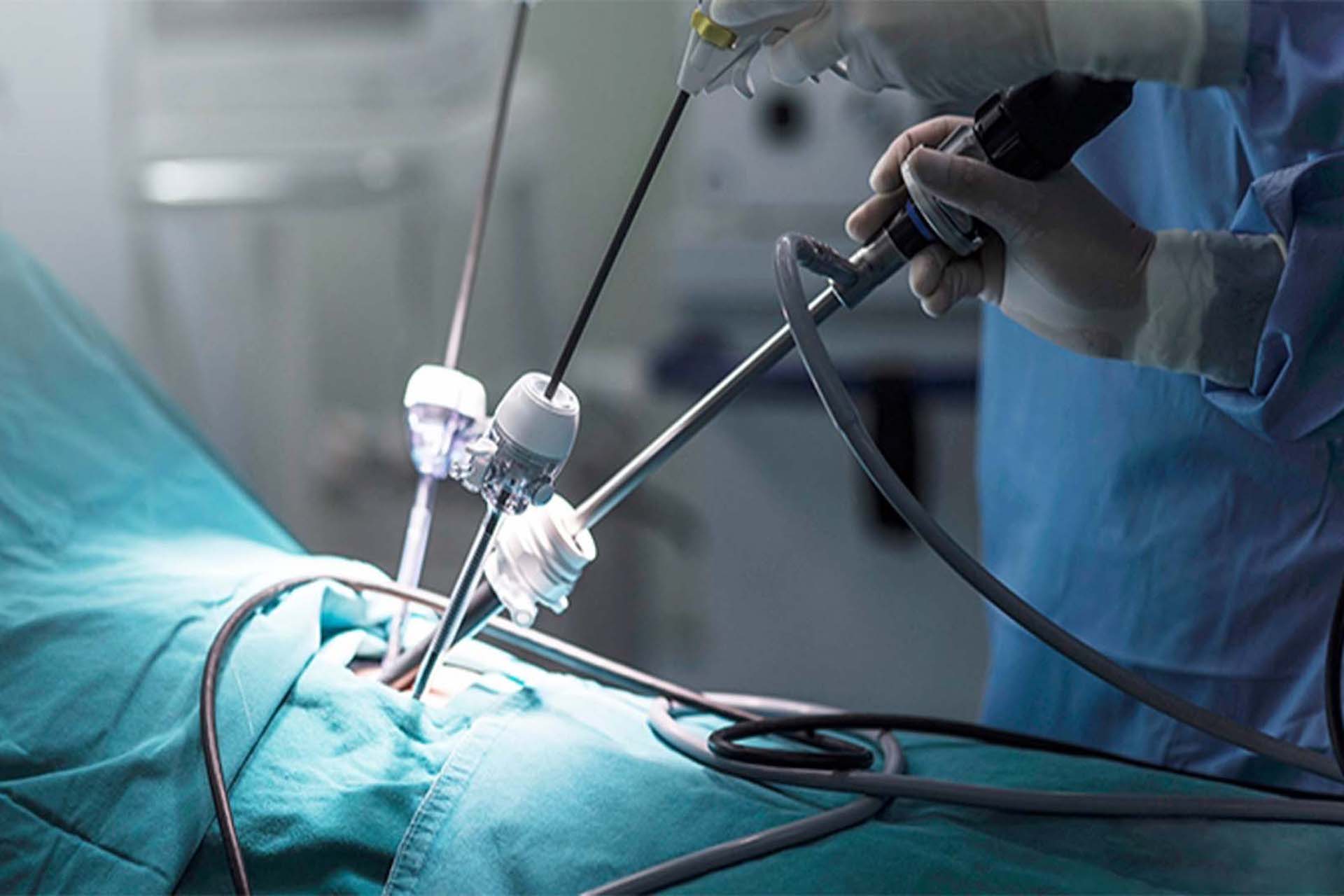
Laparoscopic surgical technique
Laparoscopic hernia surgery uses a laparoscope, a thin, flexible instrument equipped with a camera and light. It is inserted through a small incision in the abdominal wall and an image of the internal organs is shown on the monitor. This allows the surgeon to see the surgical area in detail without making a large incision.
The main stages of laparoscopic surgery:
Patient preparation
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes the necessary examinations and tests such as ultrasound, CT, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine the exact location of the hernia and assess its condition.
Create access to the abdominal cavity
After general anesthesia, small incisions are made through which the laparoscope and instruments are inserted. To ensure good visibility, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity to fill it.
Execution of the procedure
Using a laparoscope and special instruments, the surgeon carefully removes the hernial sac and closes the abdominal wall lesions. Mesh, a synthetic material that prevents hernia recurrence, is often used to reinforce the herniated area.
Completion of the procedure
Once the hernia is repaired and the mesh is secured, the laparoscope is removed and the small incisions are sutured together. The patient is transferred to the postoperative ward to recover.
Risks and complications
Like all surgical procedures, laparoscopic surgery carries certain risks and possible complications. Among them:
- Wound infection. Although the risk of infection with laparoscopic surgery is lower than with open surgery, it still exists.
- Organ damage. Damage to internal organs such as the bowel or bladder may occur during the placement of the instrument, but such cases are extremely rare.
- Recurrence of hernia. In some cases, the hernia may reappear despite the use of mesh. This may be due to the characteristics of the patient’s body or inappropriate lifestyle in the postoperative period.
To avoid or minimize complications, search for “best hernia surgeons near me” to get the best care.
Recovery after surgery
Recovery after laparoscopic surgery is generally faster than after traditional open surgery. Patients can return to normal activities a few days after surgery. However, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations to avoid recurrences or other complications:
- Avoid strenuous exercise for the first few weeks after surgery
- Monitor your condition and contact your doctor immediately if you experience pain, swelling, or redness
- Maintain a healthy diet to avoid constipation and unnecessary stomach tension
The bottom line
Laparoscopic hernia surgery is a modern, effective, and safe treatment method that significantly improves patients’ quality of life. It combines minimal injury, fast recovery, and high accuracy, making it the preferred option for many patients.






























No Comments